Artificial Intelligence has become the defining story of our decade. Models generate text, build code, compose music, analyze medical records, and orchestrate global workflows. Yet behind every prompt, every answer, and every insight produced by systems like ChatGPT, there is a silent engine consuming vast amounts of energy.
As AI gets smarter, faster, and more integrated into daily work, it is also accelerating the demand for power at a rate that many industries are struggling to comprehend. The next AI revolution will not only run on data. It will run on electricity. That shift has enormous implications for energy companies, and more importantly for the people who will operate and maintain the infrastructure that keeps AI alive.
Every Prompt Consumes Power
A typical AI chat looks simple. You type a question, the model responds, and the conversation feels effortless. But the computation behind this exchange is anything but small.
Recent estimates show the following:
- A single ChatGPT style query consumes between 0.5 watt hours to 2.9 watt hours depending on the model size and server load.
- A complete conversation of ten prompts can consume the energy of running a standard LED bulb for several minutes.
Google’s research indicates that large language model inference can require up to 10 times more energy per request than a traditional web search. Training one frontier model can consume electricity equivalent to powering 5,000 average homes for an entire month.
AI Needs Power. Power Needs People.
The surge in AI adoption means an equally massive surge in the need for energy generation, transmission, and grid reliability. Utilities, power plants, substations, distribution networks, and renewable energy farms will all face new pressures:
- Increased peak loads fueling AI data centers
- Upgrades to transmission lines to support constant high demand
- Greater stability and redundancy requirements
- Rapid deployment of new capacity including solar, wind, and battery storage
And behind all these systems is a growing workforce.
Energy companies are already experiencing workforce shortages across electrical operations, maintenance engineering, grid operation, turbine servicing, and thermal plant operations. The boom triggered by AI will intensify that shortage.
Why Training Becomes the Weakest Link
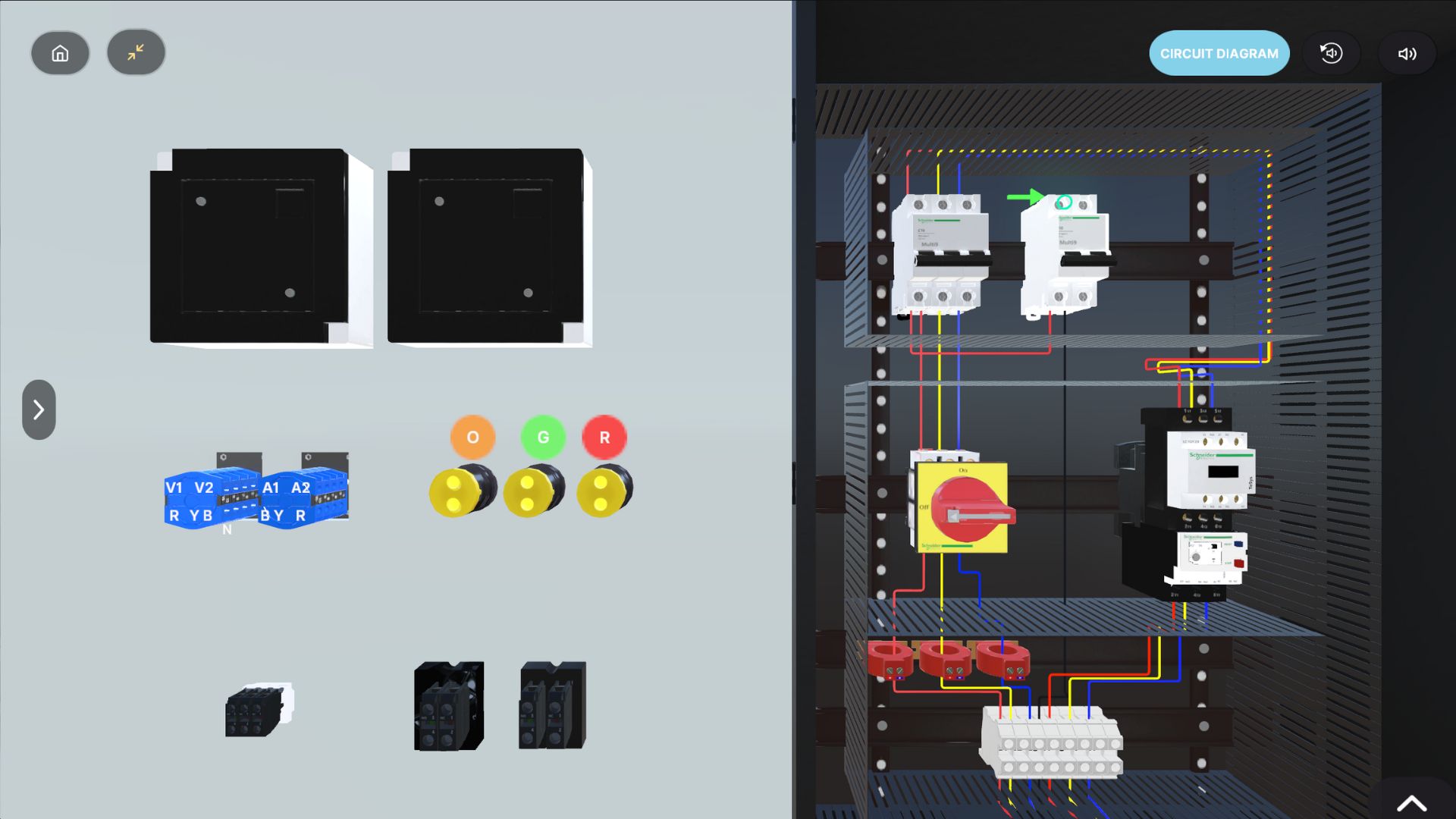
Power generation and utility operations rely on strict Standard Operating Procedures. These are precision based tasks where a single mistake can lead to shutdowns, equipment damage, blackouts, and in some environments even loss of life.
The workforce entering the industry will be younger and less experienced. Many will be joining during a rapid expansion phase with accelerated onboarding timelines.
The challenge becomes clear:
- How do you train large batches of recruits quickly?
- How do you ensure they retain procedural knowledge?
- How do you prepare them for high risk environments before they step into the real plant?
- How do you deliver training consistently across multiple locations as the sector expands?
VR Training Is No Longer Optional for Power Companies
Virtual Reality is no longer a gadget. It has matured into a scalable, high fidelity simulation technology capable of replacing 60 to 80 percent of traditional safety and SOP training.
For power companies facing the AI demand surge, VR training solves the bottleneck in four critical ways:
- Scalable training that keeps pace with hiring – One VR module can train hundreds of workers across geographies without scheduling constraints.
- Real world replication without risk – Recruits can practice operating breakers, handling isolations, managing lockout tagout procedures, navigating substations, or responding to emergencies in a safe simulated environment.
- Consistency in SOP delivery – Every trainee receives the same instruction, the same scenario, and the same performance evaluation. No variability between instructors or classrooms.
- Faster time to competency – Studies show that VR learners can retain up to 75 percent more information during safety training and achieve job ready competence 30 to 40 percent faster.
The companies that adopt VR training now will be the ones ready when AI driven electricity consumption reshapes global energy demands.
AI Is Changing the Energy Sector. VR Will Change Its Workforce.
AI will continue to evolve, and with it the world’s dependence on uninterrupted and ever expanding energy infrastructure. The next decade will reward power companies that modernize their training systems early. It will also expose those that rely on outdated methods that cannot scale, cannot replicate real world complexity, and cannot prepare a new generation of technicians for high risk environments.
As the energy sector prepares for the surge in electricity demand driven by AI, the need for scalable, reliable, and consistent workforce training has never been more urgent.
To explore how immersive, device connected VR training can support large scale workforce readiness, book a demo with Spatio.